Matula Thoughts June 4, 2021
2883 words
SUNRISES AND SUNSETS
One.
Sunrise, sunset. Nearing the halfway point of the calendar year, a favorite yearly milestone is approaching – the summer solstice and the first day of astronomical summer. As a resident years ago I didn’t much notice this longest day of sunlight but, now getting on in life, it has gained greater attention. You don’t have to go to Stonehenge to understand the Earth’s shape and tilt (23.5 degrees from orbital plane), seeing how the “easterly” position of sunrise changes from winter to summer. The sun rises in true east and sets exactly in true west only on two days each year – the equinoxes on March 21 and September 21.
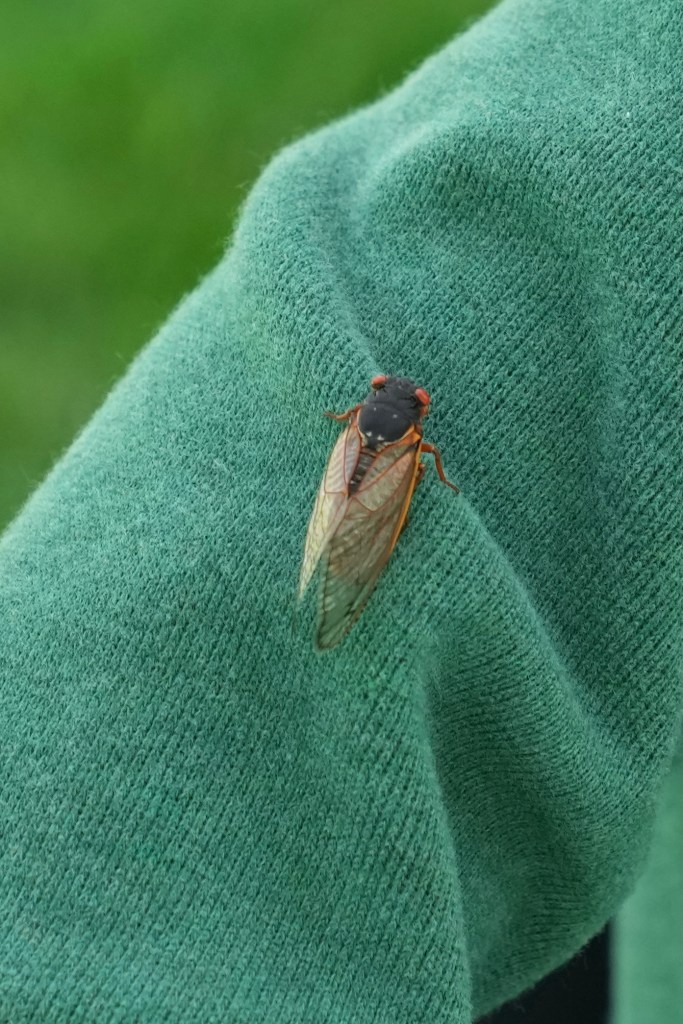

The 17-year cicadas are back. I saw and heard them on this past Memorial Day weekend. Sunrise and sunset for them span 17 years, a rather unusual existence.
Gray Michigan winters often obscure the daytime sun and we relish it when dominates in the spring. In northern Michigan summer sunsets after 10 in the evening are worth staying up to see. On Sunday June 20 summer solstice will happen at 11:31 PM EST [Below: summer sunset, Empire, Michigan.]

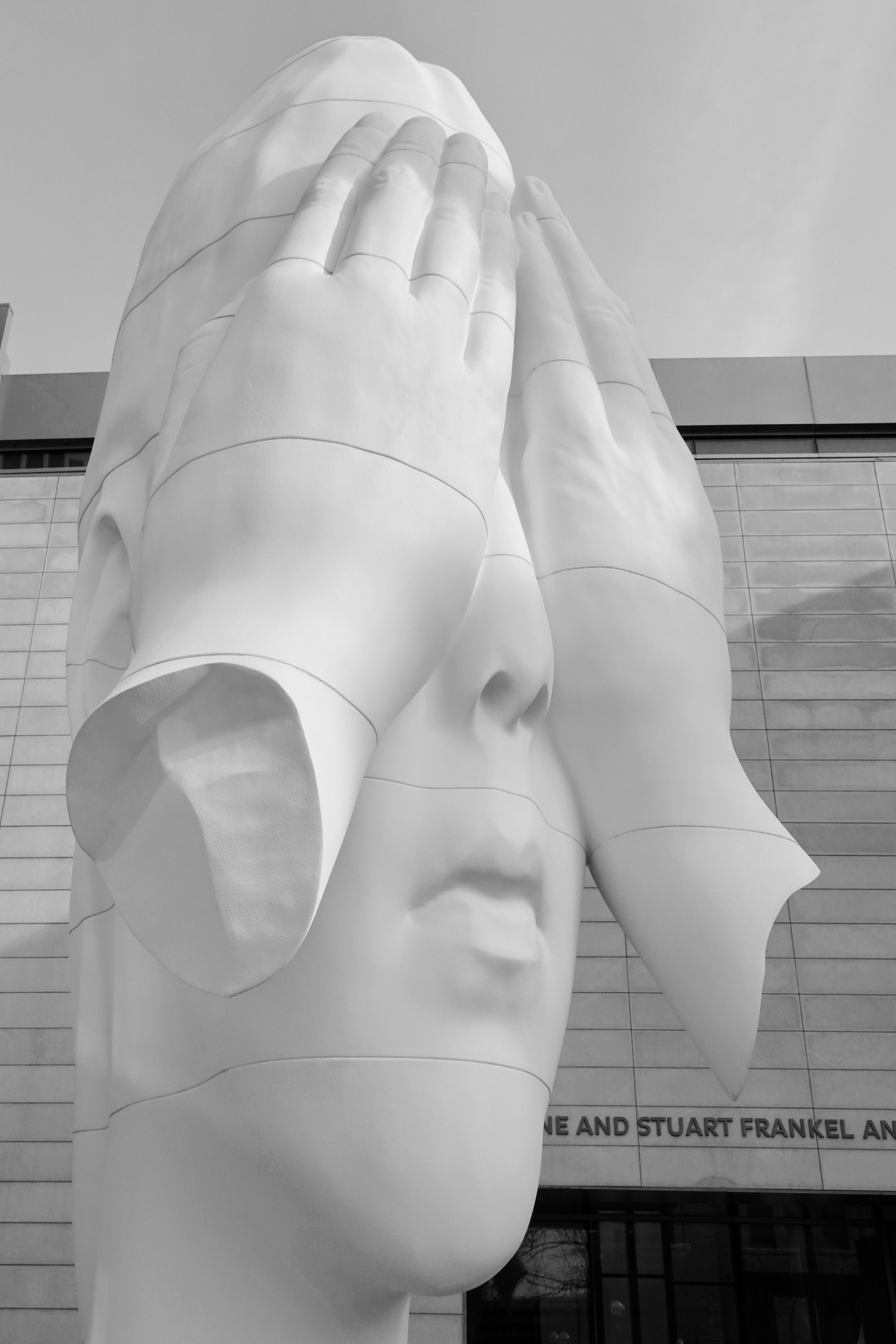
Most people believe this is true: the earth is round and it revolves around the sun. These ideas seemed counter-intuitive to pre-scientific people and even recently have been contested, but Copernican evidence for heliocentricity and Hubble Space Station observations are good enough for most people, even though some doubters still exist. They may doubt because they truly haven’t figured it out – or they hang on to the belief because it is expedient to their interests, perhaps in the sense that Jaume Plensa’s figure, Behind the Walls, suggests in front of the UM Museum of Art.
Another point to celebrate in the June calendar is the 19th, a date I’ve just learned about from a book called On Juneteenth by Annette Gordon-Reed. This was a significant moment in time, when the actuality of the Civil War concluded in Texas, thatapp had continued to fight on months after Appomattox. There is reason to think that this date may grow into a full national holiday in recognition of the still-lingering conflict over the opening of the second paragraph of the Declaration of Independence.

Two
Words cannot express … Pandemics don’t fit into calendar years neatly and it turns out that any expectations that Covid-19 would last only a year were naïve, now that we are well into a second year. Yet, incredibly in this relatively short time, have developed vaccines and better skills at managing the active disease. Few of us have not seen covid up front in friends, family, patients, and neighbors – whether in acute disease, long-haulers, or death. While covid death has largely spared the UM urology family, mortality at-large has not. [Above: Eclipse, Alma Thomas, 1970. SAAM.]
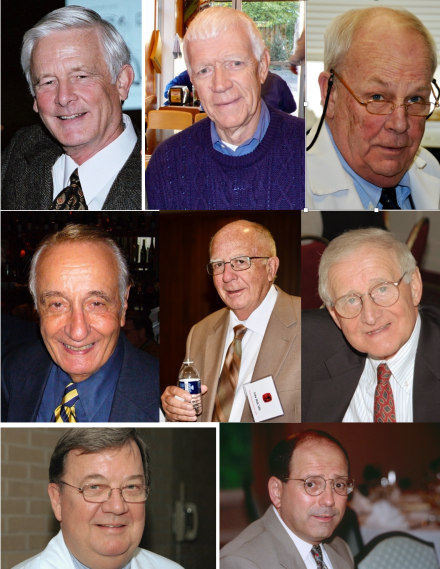

In this past year of social submergence we have lost Ed Tank, Clair Cox, Dick Dorr, Ed McGuire, Bob Moyad, John Hall, Joe Cerny, and Bill Belville (shown in rows from top left, above) amidst other personal and patient losses, and certainly there will be more. Each loss creates a unique reconciliation for each of us, and when writing condolence notes the phrase “words cannot express …” often comes to mind, even if left unwritten. Some words, particularly those of poets, however, do come closer to the mark of replicating feelings.
A recent web-based reading and discussion with two great American poets, Edward Hirsch and our UM colleague Linda Gregerson, was particularly rich in meaning. It was sponsored last month by The Book Stall in Winnetka, IL, to plug Hirsch’s new book, 100 poems to Break Your Heart, and it included a piece by Linda, For the Taking, that she read. She had sent me a link to the event and any chance to hear her perform a reading is worth the price of admission. Hirsch’s title is far from inviting, but the book contains much that gets close to the mark in expressing grief in words, authentically. The introduction offers a framework for an enabling understanding of grief.
“Implicit in poetry is the notion that we are deepened by heartbreaks, by the recognition and understanding of suffering – not just our own suffering but also the suffering of others. We are not so much diminished as enlarged by grief, by our refusal to vanish, or let others vanish, without leaving a verbal record. The poet is one who will not be reconciled, who is determined to leave a trace in words, to transform oceanic depths of feeling into faithful nuances of art.”
This paragraph rings true, the process of dealing with grief, Hirsch says, not only reconciles but also painfully enlarges us. This point extends beyond personal needs to console ourselves with personal losses and express condolences to others for their personal losses – we also need to develop the vocabulary and nonverbal skills in our medical students and residents because dealing with grief is a life skill that physicians need and cannot be delegated to our few palliative colleagues. Maybe some of us know this implicitly, but I for one really didn’t fully comprehend this idea until Hirsch’s book.
Three.

Heliocentricity was believed a factual truth by some people in classical antiquity, ancient India, the medieval Islamic world, and Renaissance thinkers (da Vinci: “The Sun does not move.”) but it was Copernicus in 1543 who largely settled the question, or so it seemed. Galileo’s observations and calculations made him a champion of Copernican heliocentricity although leaving the Italian astronomer at odds with the Roman Church. An Inquisition in 1615 supported the Church’s defense of faith against science, but Galileo continued to challenge authority. His book in 1632, Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systemscompared the Copernican system with the traditional Ptolemaic system and was construed as a challenge to the Pope the final straw to bring the Church down on Galileo. An Inquisition in 1633 confined Galileo to house arrest for the last years of his life. [Above: Andreas Cellarius (1596-1665) illustration of the Copernican system, from the Harmonia Macrocosmica.]
Even after the Church gave up the fight against heliocentrism, others took up the ignoble battle. In 1859 Commander A.J. Morison published a book The New Principia; or True System of Astronomy, in which Earth is proved to be the Stationary center of the Solar System … while the Sun travels yearly in an ellipse around the Earth. He wasn’t the last to hold this retrograde notion, an author with the curious pseudonym Parallax in 1873 published Zetetic Astronomy, Earth is not a globe. An Experimental Inquiry into the true figure of the Earth, proving it a plane … and the only known material world. The 20th century began in 1901 with more support for these enduring memes, with Wardlaw S. Scott’s, Terra Firma: The Earth is Not a Planet, proved from Scripture, reason and fact.
False claims of Morison, Parallax, and Scott – whether delusional beliefs or blatent commercial propoganda – were out of step with the accumulated world view and evidence of science. Yet, as testimonies to free speech, they were offered fairly to the public that in turn rendered public opinion and scientific evidence that deemed the Flat Earth claims ludicrous then, a century past – and even more so in this day and age. Nevertheless, as the human population nears eight billion it is no surprise that some small minority will embrace these ancient delusions as a startling reality. Autocracies protected from free speech can demand such delusions for its nation.
The recent phenomenon of instantaneous global social media clouds the issue, allowing deliberate false claims of rumors, conspiracy theories, or alternate realities to infect huge swaths of the population within minutes, imperiling truth. The matter of free speech, held so dearly until now by liberal democracy, is in question today as never before – yet, as always, some limits to free speech have always been recognized, such as “yelling fire in a crowded theater,” an example hard to come by in Covid times.
Four.
Politics – local and larger. The Covid Pandemic of 2020 continues to diffuse into 2021, further disrupting lives, businesses, economies, education, health care, and so on but just as any crisis this one brings some old problems into focus with new clarity. Health care disparities, in the grossest sense of greatly increased death rates in disadvantaged communities, is one salient example. Less glaring, but no less concerning, is the rampant spread of misinformation (whether imagined or malign) and the inability of wide swaths of the population to comprehend a proper and reasonable scientific argument. These two matters (among others) are serious threats to the human future.
If a democracy is to reflect the corporate beliefs and aspirations of a populace in maintaining its rules and regulations, it stands to reason that the populace must be reasonably literate – holding, forming, and reforming beliefs that are reasonable, drive toward truth, and promote the civilized behaviors upon which civilization depends. In past centuries when civilization was primarily a local phenomenon and information was finite, autocratic governance worked well enough, until it didn’t and was replaced by new authorities. When enough of the population was fed up, or not fed enough, change happened as after Marie Antoinette said to her hungry subjects, “Let them eat cake.” The will of the people tipped her off the throne. Some sort of quorum-sensing formula, driven by hunger, inequity, abuses, or other outrages turns a compliant population into an angry one that demands change. This biological behavior transcends the animal kingdom.
It’s gotten more complicated for human civilization that has progressed from a three-dimensional world to a world with a fourth dimension of information that accelerated after Gutenberg and jumped into warp speed with the digital revolution and the internet. – information, and that information is infinite. The Shannon number comes to mind, a calculation by Claude Shannon indicating the number of possibilities of the game of chess. This number far exceeds the number of number of atoms estimated in the observable universe, an enormously huge number itself, and yet the Shannon calculation represents only a single game in the incalculable pantheon of human knowledge.
Civilization today is largely experienced globally, with a mix of inter-connected governmental systems, although all governments ultimately, in one way or another, depend on some corporate consensus of belief in them, whether the ruling authorities are autocratic, sectarian, democratic, military, “divinely ordained” royalty, or otherwise in the position of authority. Nevertheless, regardless of the fourth dimensionality and globalization, the basic biologic determinants prevail and quorum sensing of pain and outrage continue to tip the scales of political equilibrium, but with more destructive consequences than machetes, guillotines, or guns.
Five.
Literacy. This idea relates to two papers sent to me – one by our colleague Cliff Craig, UM Professor of Orthopedics and the other from his 1965 UMMS classmate Mike Johns, now in Atlanta after stints at Johns Hopkins, Emory, and back at UM as interim EVPMA.
The first, a JAMA paper by neurologist at Indiana University Bruce Miller, discussed false responses to the Covid pandemic. [B.L. Miller. “Mechanisms and Possible Responses.” JAMA. 2020;324 (22): 2255-2256.] Miller rightly stresses the importance of Science Literacy, but as I read the story that term Science Literacy jumped out at me. It’s not a new term, having been around for a century in various forms, but it became prominent in conversation and literature after around 1970, when it was viewed as an extraordinary form of literacy. Paul de Kruif, a UM Ph.D. and assistant professor in microbiology, in microbiology was one of the early “science writers” for general audiences.
At the most basic level, literacy is the ability to read and write, uniquely human skill sets and arguably the product or cause of civilization. Very quickly in the course of civilization literacy came to mean three things, the “three Rs,” reading, writing, and arithmetic. St. Augustine of Hippo , writing in Latin around AD 400 confessed the importance of “legere et scribere et numerare discitur” (learning to read, and write, and do arithmetic). Now, 1700 years after St. Augustine, it is no less appropriate to exclude Scientific Literacy from the core properties of literacy than it would have been to exclude “numerare discitur” from “reading and ‘riting’”.
Our Western educational systems have largely failed, making scientific literacy a deliberate exclusion from the vast majority of educational products. We graduate students from universities with literacy in literature, performance, art history, accounting, business, law, world history, music, marketing, packaging, political science, languages, and even in engineering, scientific, and health care professions without a firm basis in scientific literacy in its largest sense: how do we hold, form, and reform beliefs based on science and general human values.
The second paper was more complex and required deeper reading. In fact, that’s what it was about – deep reading. This paper by Adam Garfinkle in National Affairs, in fact required a couple of runs through it myself and while it dealt with literacy, it approached the topic through a consideration of neural pathways. [National Affairs, Spring, 2020.] Deep literacy, Garfinkle claims, builds capacity for abstract thought, analysis of difficult questions, imagination, creativity, clarity, and empathy. Language is at the core of this phenomenon of deep literacy, that goes far beyond its basic platform of the “three Rs.” The author ties this into biology, culture, and political systems.
“Deep reading has in large part informed our development as humans, in ways both physiological and cultural. And it is what ultimately allowed Americans to become ‘We the People,’ capable of self-government. If we are losing the capacity for deep reading, we must also be prepared to lose other, perhaps even more precious parts of what deep reading has helped to build.”
The risk to deep literacy seems to come from the loss of quality attention – some call this “cognitive patience.” The digital revolution is blamed for this, but it may be a larger 20thcentury phenomenon tied in with its faster pace of culture, manifested in work, entertainment, news cycles, and travel. The search engines have increased the pace, and with smart phones, tablets, and computers by our sides we may not need to teach memorization of multiplication tables or speeches such as the Gettysburg Address. Yet something happens in the human brain when the tables are learned and when the speech is memorized – internalized, as it is. By off-loading or sub-contracting the mental work of processing facts, ideas, and narratives, we may lose the ability to synthesize from them.
Musical literacy and that of visual art differ from the art of numbers and narratives. Knowing the multiplication tables and Gettysburg Address, for example and for most people, require mental work – the brain must expend calories to accomplish those tasks. Somehow it takes less work to internalize a tune or recall a picture. American Pie and Mona Lisa are carried around by most people of my vintage and in my region of space. A musician or painter can build upon them, consciously or subconsciously, when they create something new. The same is true for someone who really knows the Gettysburg Address, but it’s one thing to really know all 172 words and another thing to call it up from Wikipedia or Alexa.
Postscript.
Sunrise, Sunset was the wedding song written in 1964 by composer Jerry Bock and lyricist Sheldon Harnick for the musical play, Fiddler on the Roof. It hit close to the mark as Harnick recalled at age 90 in an NPR interview April 30, 2014.
“I do remember when we wrote “Sunrise Sunset,” the first person we played it for was Jerry Bock’s wife. And when I perform a song for someone I try not to look at them. It makes me a little upset if they’re not paying attention. So I look above them or to the side of them.
Anyway, I sang “Sunrise Sunset” and when I finished, then I looked at Jerry’s wife Patti and I was startled to see that she was crying. And I thought my goodness; this song must be more effective than we even know. And the same thing happened – I am not a pianist but the music to “Sunrise Sunset” is easy enough so that I could learn the piano part – and I played it for my sister.
And when I finished I looked and she had tears in her eyes. And that was a very unusual experience.”
The song still rings true. [Below: Summer sunset, Empire, Michigan.]

Matula Thoughts began about 20 years ago in the form of a monthly email What’s New from the Medical School Dean’s Office of Faculty Affairs and transitioned to a Urology Department monthly communication around 2007. In 2013 the personal essay took the form of Matula Thoughts, on a web site called Word Press, and this essay is around the hundredth in that form. There is a time for all seasons and this seems the right time to “sunset’ this public effort, but with great appreciation to the readership that motivated me for the past two decades. The monthly discipline of producing Matula Thoughts has been invigorating but this seems the right time to let it go.
Thank you if you’ve been following Matula Thoughts over these years.
David A. Bloom, June 4, 2021